DNA Sequencing
BIO332 Applied Bioinformatics
Prof. Harbert
DNA Sequencing: Overview
The ability to sequence DNA is one of the greatest achievements of the field of Biology.
We will talk today about some of the history of DNA sequencing and the main technologies involved today.
Topics:
Traditional Technology
- Sanger Sequencing
- The Human Genome Project
Massively Parallel DNA Sequencing (formerly Next Generation Sequencing)
- Illumina
- PacBio
- NanoPore
Sanger
Dr. Frederick Sanger (1918-2013) -- Developed sequencing by the chain terminating dideoxynucleotide method that now carries his name.

Sanger
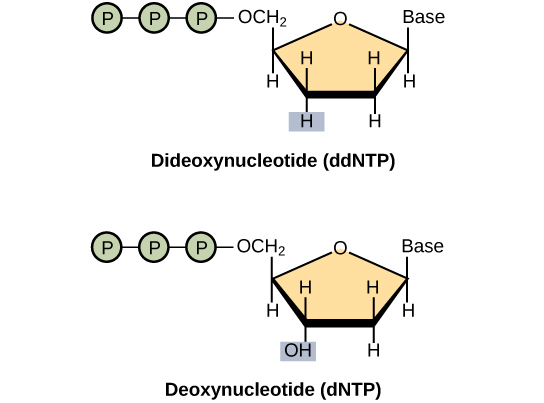
Image credit: "Whole-genome sequencing: Figure 1," by OpenStax College, Biology (CC BY 4.0)
Sanger
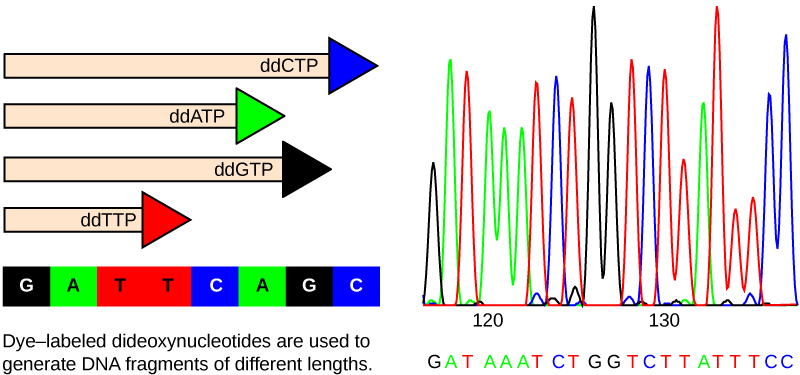
Image credit: "Whole-genome sequencing: Figure 1," by OpenStax College, Biology (CC BY 4.0)
Sanger
Sanger
Sanger
Produces high quality reads
- Length: 400-600 bp (sometimes longer to ~1kbp)
- High base call accuracy (>95% and relatively easy to detect).
- Maxes out at about 384 reads per run on typical equipment (some of this can be automated) due to lab infrastructure constraints.
- A few hours per run
- Applied Biosystems equipment
How many runs at 500bp per read and (let's assume) 384 reads per run would it take to sequence the human genome at 3 billion bases one time?
Human Genome Project
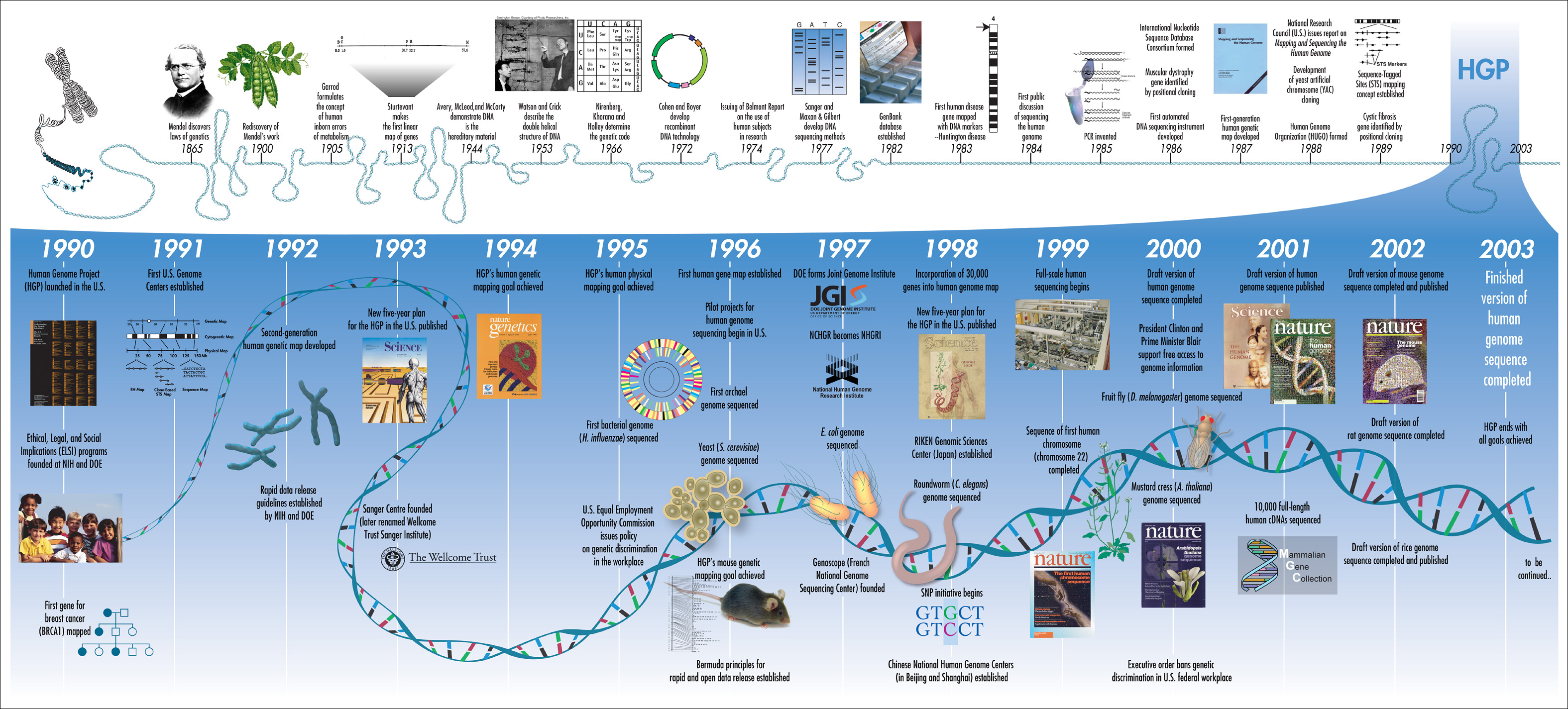
Current Sequencing Technology:
Illumina
PacBio
PacBio
Ion Torrent
Oxford Nanopore
More Nanopore
Introduction to nanopore sequencing from Oxford Nanopore on Vimeo.
Other Resources
Library prep and Illumina Seq: http://rmpiro.net/teaching/pub/lectures/fu-genomics/01-NGS_technology.pdf
Review of sequencing platforms (2017): https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/generations-of-sequencing-technologies-from-first-to-next-generation-0974-8369-1000395.php?aid=87862